183. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits^\frac\pi4_0 (2sec^2x +x^3 + 2)dx\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain

184. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits ^\pi_0\left(sin^2\frac x2 - cos^2 \frac x2\right)dx\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain

185. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits^2_0\frac{6x + 3}{x^2 + 4}dx\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain

186. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits^1_0\left(xe^x+ sin \frac{\pi x}{4}\right)dx\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
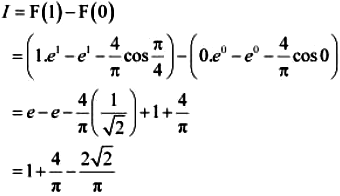
187. \(\int\limits^\sqrt 3_1 \frac{dx}{1 + x^2}\) equals
A. \(\frac \pi3\)
B. \(\frac {2\pi}3\)
C. \(\frac \pi6\)
D. \(\frac \pi{12}\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain

Hence, the correct Answer is D.
188. \(\int\limits^\frac23_0 \frac{dx}{4 + 9x^2}\) equals
A. \(\frac \pi6\)
B. \(\frac \pi{12}\)
C. \(\frac \pi{24}\)
D. \(\frac \pi{4}\)
Answer:

By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain

Hence, the correct Answer is C.
189. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits ^1_0 \frac x {x^2 + 1}dx\)
Answer:
\(\int\limits ^1_0 \frac x {x^2 + 1}dx\)
Let x2 + 1 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt
When x = 0, t = 1 and when x = 1, t = 2

190. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits ^{\frac\pi2}_0\sqrt{sin \phi}\,cos^5 \phi d\phi\)
Answer:
Let \(I=\int\limits ^{\frac\pi2}_0\sqrt{sin \phi}\,cos^5 \phi d\phi=\int\limits ^{\frac\pi2}_0\sqrt{sin \phi}\,cos^4\, cos \phi \,d\phi\)
Also, let
\(sin \phi = 1 \)
⇒ \(cos\phi\, d\phi = dt\)

191. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits^1_0 sin^{-1} \left(\frac{2x}{1 +x^2}\right)dx\)
Answer:
Let \(I=\int\limits^1_0 sin^{-1} \left(\frac{2x}{1 +x^2}\right)dx\)
Also, let x = tanθ ⇒ dx = sec2θ dθ
When x = 0, θ = 0 and when x = 1, \(\theta = \frac\pi4\)

Taking θ as first function and sec2θ as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain

192. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits_0^2 x \sqrt{x + 2} \,(\text{Put } x + 2= t^2)\)
Answer:
\(\int\limits_0^2 x \sqrt{x + 2dx} \)
Let x + 2 = t2
⇒ dx = 2tdt
When x = 0, t = √2 and when x = 2, t = 2

193. Integrate the function:
\(\int \limits^\frac\pi2_0 \frac {sin\, x}{1 + cos^2 x}dx\)
Answer:
\(\int \limits^\frac\pi2_0 \frac {sin\, x}{1 + cos^2 x}dx\)
Let cos x = t
⇒ −sinx dx = dt
When x = 0, t = 1 and when \(x = \frac\pi2, t = 0\)

194. Integrate the function:
\(\int\limits^2_0 \frac{dx}{x + 4 - x^2}\)
Answer:

Let \(x - \frac12 = t\) So dx = dt

