1. Cyanohydrin –
It is a compound which contain both OH and CN groups.
For example, Lactic acid can be obtained by hydrolysis of cyanohydrin.

2. Acetal –
compounds formed by the reaction of aldehydes with monohydric alcohols in presence of dry HCI gas.

3. Semicarbazone –
the product of carbonyl compounds with semicarbazide is known as semicarbazone.

4. Aldol –
It is a condensation product of aldehydes or ketones having at least one α – hydrogen atom with dilute alkali as catalyst.

5. Hemiacetal –
It is a compound which contains an ether as well as alcohol functional group.
For example, methoxyethanol is a hemiacetal.

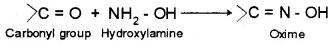
6. Oxime –
Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine.
7. Ketal –
It is a cyclic compound obtained by reaction of aceone with ethylene glycol.

8. Imine –
Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with ammonia.

9. 2, 4-DNP derivative –
2, 4-phenylhydrazone (DNP) is the addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.

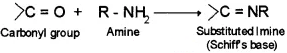
10. Schiff’s base –
Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with amine.