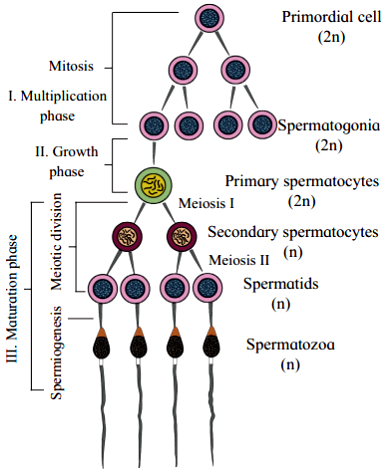
(1) The process of spermatogenesis takes place in the male gonads or testis. The cells of germinal epithelium that line the seminiferous tubules undergo spermatogenesis.
(2) Primordial germ cells or germinal cells pass through three phases, viz. phase of multiplication, phase of growth and phase of maturation.
- Multiplication phase : Primordial germ cells undergo mitotic divisions to produce many diploid (2n) spermatogonia.
- Growth phase : Spermatogonium accumulates nutrients and grows in size, giving rise to primary spermatocyte (2n).
- Maturation phase : The primary spermatocyte undergoes first meiotic division or maturation division. Exchange of genetic material occurs between homologous chromosomes in each spermatocyte.
(3) The meiotic division gives rise to secondary spermatocyte which is haploid (n). At the end of first meiotic division two secondary spermatocytes are formed while at the end of second meiotic division four haploid spermatids are formed.
(4) Spermatids are non-motile. They undergo spermiogenesis and form motile spermatozoan (sperm).
(5) The changes taking place during spermiogeneis are as follows:
- Increase in length.
- Formation of proximal and distal centriole.
- Distal centriole forms the axial filament.
- Mitochondria become spirally coiled.
- Acrosome is formed from Golgi complex.