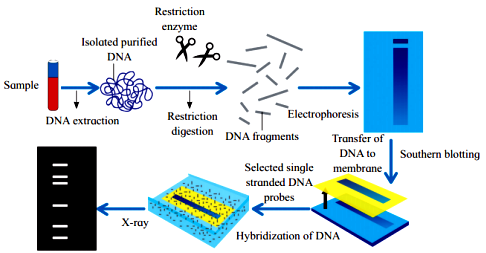
Steps involved in DNA fingerprinting are as follows:
1. Isolation of DNA : The DNA can be isolated even from the small amount of tissue like blood, hair roots, skin, etc.
2. Restriction digestion:
- The isolated DNA is treated with restriction enzymes which cut the DNA at specific sites to form small fragments of variable lengths.
- Variations in the lengths of restriction fragments are known as Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP).
3. Gel electrophoresis:
- The DNA samples are loaded on agarose gel and electrophoresis is carried out.
- Negatively charged DNA fragments move to the positive pole.
- Separation of fragments depends on their length and it results in formation of bands.
- dsDNA is then denatured into ssDNA by alkali treatment.
4. Southern blotting : The separated DNA fragments are transferred to a nylon membrane or a nitrocellulose membrane.
5. Selection of DNA probe:
- DNA Probe is a known sequence of single- stranded DNA.
- It is obtained from organisms or prepared by cDNA preparation method.
- The DNA probe is labelled with radioactive isotopes.
6. Hybridization:
- In this process, probe is added to the nitrocellulose membrane containing DNA fragments.
- The single-stranded DNA probe pairs with the complementary base sequence of the DNA strand.
- As a result DNA-DNA hybrids are formed on the nitrocellulose membrane. Unbound single-stranded DNA probe fragments are washed off.
7. Photography : The nitrocellulose membrane is then kept in contact with X-ray film. DNA bands, due to radioactive probe, give photographic image on X-ray film. This is autoradiography.