(A) Principle :
(1) The lead accumulator is a secondary electrochemical cell since electrical energy and emf are not developed within the cell but it is previously stored by passing an electric current. Hence it is also called lead accumulator or lead storage battery.
(2) It is reversible since the electrochemical reaction can be reversed by passing an electric current in opposite direction and consumed reactants can be regenerated.
(3) Hence battery can be charged after it is discharged.
(B) Construction : In a lead accumulator, the negative terminal (anode) is made up of lead sheets packed with spongy lead, while the positive terminal (cathode) is made up of lead grids packed with PbO2.

Sulphuric acid of about 38% strength (%w/w) or specific gravity 1.28 or 4.963 molar is the electrolyte in which the lead sheets and lead grids are dipped. The positive terminal and negative terminal are alternatively arranged in the electrolyte and are separately interconnected.
(C) Representation of lead accumulator :

(D) Working of a lead accumulator :
(1) Discharging :
When the electric current is withdrawn from lead accumulator,
The following reactions take place :
Oxidation at the – ve electrode or anode :
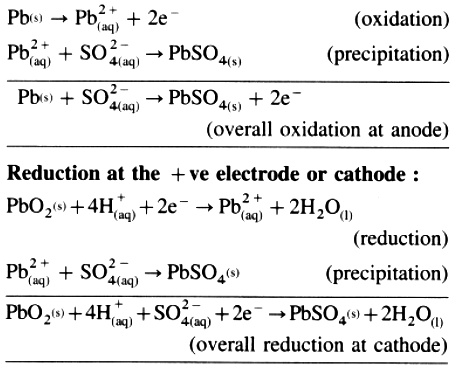
(2) Net cell reaction :
(i) Thus, the overall cell reaction during discharging is

OR
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(I)
The cell potential or emf of the cell depends upon the concentration of sulphuric acid. During the operation, the acid is consumed and its concentration decreases and specific gravity decreases from 1.28 to 1.17. As a result, the emf of the cell decreases. The emf of a fully charged cell is about 2.0 V.
(ii) Recharging of the cell : When the discharged battery is connected to external electric source and a higher external potential is applied the cell reaction gets reversed generating H2SO4.
Reduction at the – ve electrode or cathode :
PbSO4(s) + 2e- → Pb(s) + \(SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}\)
Oxidation at the + ve electrode or anode :
PbSO4(s) + 2H2(I)O → PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + \(SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}\) + 2e-
The net reaction during charging is,
2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(I) → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + \(SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}\)
OR
2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
The emf of the accumulator depends only on the concentration of H2SO4.
(E) Applications :
1. It is used as a source of d.c. electric supply.
2. It is used in automobile in ignition circuits and lighting the head lights by connecting 6 batteries giving 12V potential.
3. It is also used in invertors.