F) Spore Formation:
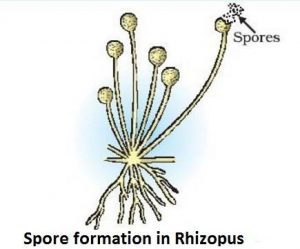
- This mode of asexual reproduction which is mainly observed in non-flowering plants.
- The parent plant produces hundreds of tiny spores and each spore give rise to a new plant.
- Some fungi (Rhizopus) and bacteria exibits spore formation.
Sexual Reproduction:
- When there is involvement of two parents to produce their young ones similar to them. Then this mode of reproduction is called sexual reproduction.
- Both male and female gametes are involved to reproduce.
- Either the same individual or by different individuals of the opposite sex these gametes are formed.
- Sexual reproduction incorporates a process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants:
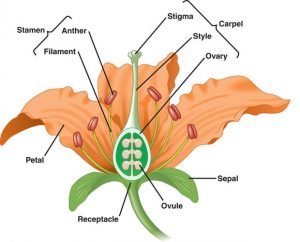
- The different parts of a flower are – sepals, petals, stamens and carpels.
- The reproductive parts of a flower are stamens and carpels.
- Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces yellow colored pollen grains.
- Carpel is the female reproductive part and is present in the centre of a flower. It consists of three parts, they are ovary, style and stigma.
- In ovary there is ovules and each ovule contains an egg cell.
- Pollen grains produce male germ-cell which fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule.
- The fusion of the germ-cells (fertilization) forms the zygote which grows into a new plant.
- When there is transfer of pollen grains from stamen to stigma occurs in the same flower, it is self-pollination.
- When there is transfer of pollen grains from stamen of one flower to stigma of other flower then it is cross pollination.
- The transfer of pollen from one flower to other flower is carried out by wind, water, insects or animals.
- Pollen grains after reaching stigma has to move towards female germ cells present in ovary. This is carried through a long tube which travels through the style and reaches ovary.
- After fertilisation, the zygote form an embryo within the ovule after dividing itself many times.
- The ovule develops and later converted into a seed while ovary ripens to form fruit.
- The seed after getting suitable conditions grows into a new plant, this process is called
Changes that take place in teenagers (puberty):
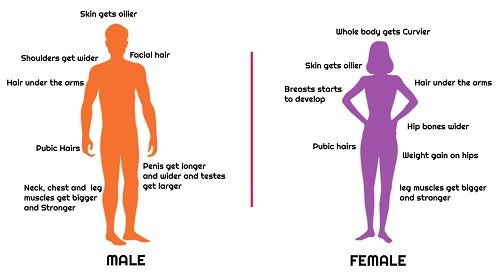
- Height and weight increases up to teenage in boys as well as girls.
- We aquire new teeth also milk teeth got broken new one take place of it.
- In boys as well as girls thick hair starts growing in armpits and the genital area between the thighs, which also becomes darker in colour.
- The skin starts becoming oily and we might begin to develop pimples.
- In girls, breast size starts increasing, with darkening of the skin of the nipples at the tips of the breasts.
- Also, menstruation cycle starts in girl.
- The facial hair of boys starts growing and voice becomes harder.
- Occasionally, the penis begins to become enlarged and erect, either in daydreams or at night.
- All the changes takes place over months, in some person these changes takes place earlier and in some after some age.
- In simple, Sexual maturation of the body starts.
- When our general body growth slows down, then reproductive tissues (sexual maturation) starts becoming mature. This period of adolescence is called
Reproduction in human:
- Human beings use sexual mode of reproduction to keep its existence on this earth.
- Reproduction in human involves germ cells of two individuals of opposite sex to join together.
- Either external release of germ-cells from the bodies of individuals or two individuals joining their bodies together for internal transfer of germ-cells is required for sexual reproduction.
- Sexually mature individuals having mature reproductive organs and breast, can take part in this process of reproduction.
- Special organs are there in humans to transfer germ cells from one body to another.
- Reproduction in animals is mainly sexual mode of reproduction.
A) Male reproductive system:
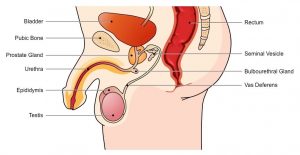
There are several parts of the male reproductive system:
- Testes or testicles:
The production of germ cells (sperms) takes place in testes. These are present outside the abdominal cavity in a bag like structure called scrotum. Sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal human body temperature. It also secretes a hormone named testosterone regulates the formation of sperms which brings changes in teenagers.
- Vas deferens:
The sperms formed in testes are transferred through the vas deferens. This tube joins with the tube coming from urinary bladder forming a common passage for both sperms and urine.
- Prostate glands and seminal vesicles:
These glands are present at the path of vas deferens. They add their secretions to the sperms to make it fluid. By this transport of sperms becomes easier. This fluid also provides nutrition.
- Sperms:
The tiny bodies that consist of mainly genetic material and a long tail that helps them to move towards the female germ-cell.
Female reproductive system:
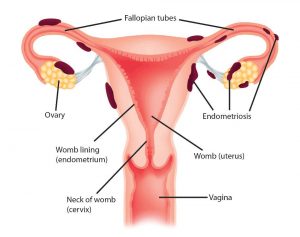
There are several parts of female reproductive systems:
1. Ovaries:
The female gamete (egg or germ cells) are formed at this site. Some hormones are also produced inside the ovaries. Egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
2. Oviducts:
These are also called fallopian tube. By this passage egg is carried from ovary to womb.
3. Uterus:
The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure called uterus. Uterus ends in vagina through cervix. It is also called womb. It supports the developing fetus during pregnancy.
4. Vagina:
The vagina is an elastic, muscular tube. It connects between cervix of the uterus to the exterior of the body. The vagina accepts the penis during sexual intercourse. It also carries sperm to the uterus and fallopian tube. It also acts as a birth canal as well as menstrual flow also exists out the body through it.
Mechanism of reproduction:
- The sperms enter inside the female body through the vagina during sexual intercourse.
- They travel in oviduct where they meet eggs.
- Now the fertilized eggs (zygote) settles in the uterus and starts dividing.
- The mother’s body is ready to undertake the development of a child.
- Uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo.
- The line of the uterus is richly supplied with blood to nourish growing embryo.
- Placenta is a special tissue in mother’s body which provides nutrition to embryo from mother’s blood.
- Villi present at the uterine wall, provides a better surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass to the embryo.
- Waste materials from embryo is removed through placenta by transferring it to mother’s blood.
- Approximately, nine months are required in the development of a child inside mother’s uterus.