(1) Carboxylic acid loses a proton as compared to phenol. Consider the ionization of carboxylic acid and phenol
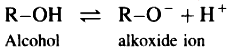

Due to delocalization the negative charge over the ortho and para positions of aromatic ring, phenoxide anion is more stable than phenol.
Thus phenol easily undergoes ionization

However,
Alcohol and alkoxide ion are single structures. In an alkoxide anion the negative charge is localized on a single oxygen atom.
Hence,
Phenols are more acidic than alcohols.
(2) Carboxylic acid has two resonance hybride non equivalent structures (I & II) while carboxylate anion has two resonance hybrid equivalent structures (III & IV).
The carboxylate ion is more stable than carboxylic acid and equilibrium is shifted towards the direction of increased ionization.

(3) Carboxylate ion has two equivalent resonance structures with nejative charge is delocalized over two electro negative oxygen atoms.
Phenoxide anion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which negative charge is delocalized over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atom.
As a result carboxylate anion is more stable than phenoxide ion.
Hence,
Carboxylic acids ionize to the greater extent than phenol furnishing higher concentration of H ions.
Therefore,
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols and alcohols.