Correct Answer - b.
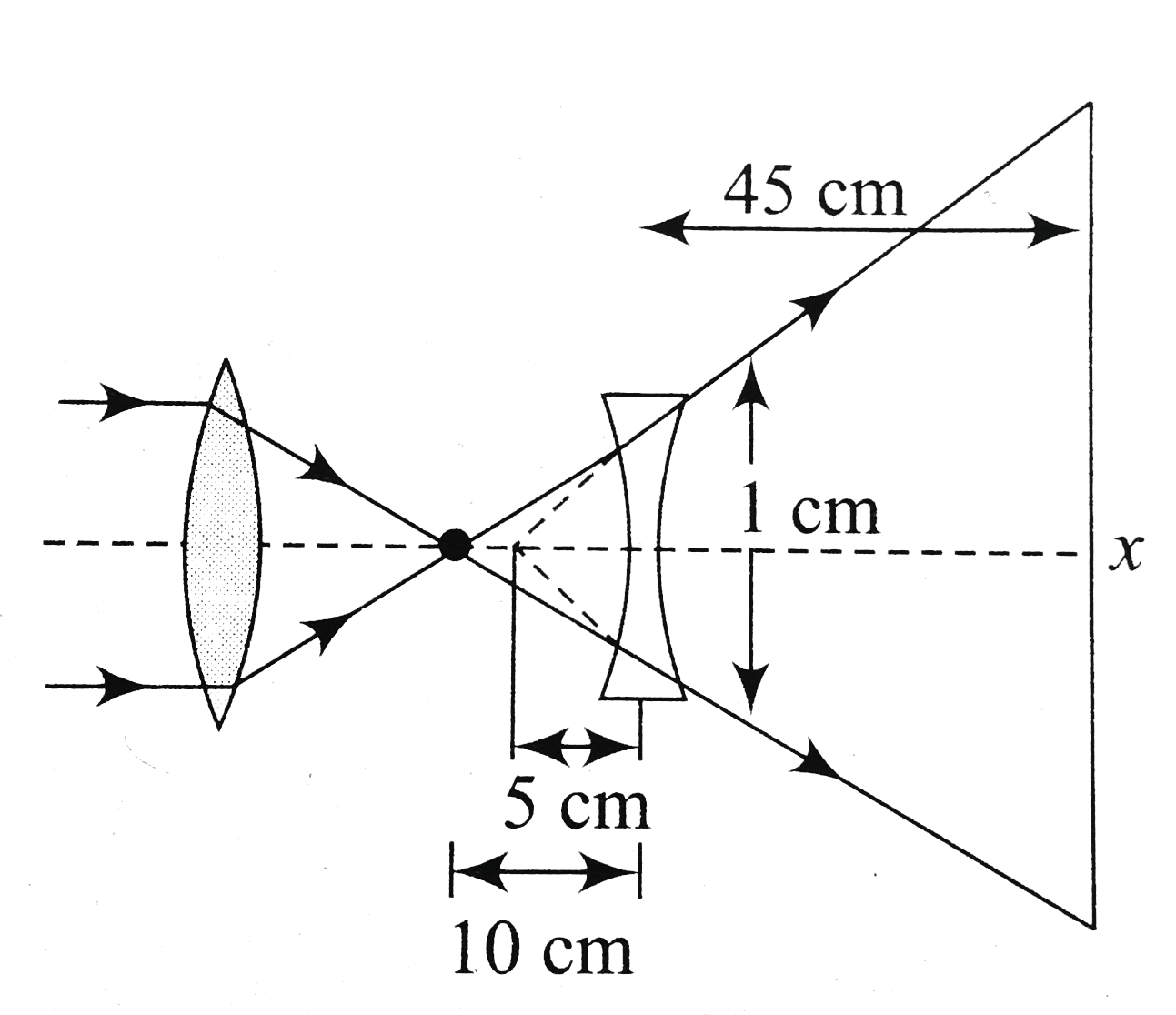
In case (a), the incident parallel beam emerges as a parallel beam. So area illuminated,
`A_(1)=pi(1)^(2)=picm^(2)`
In case (b), let x be the diameter of the area illuminated.
Then,
`(x)/(45)=(1)/(5)rArr x=9cm`
`A_(2)=pi((9)/(2))^(2)=(81)/(4)picm^(2)`
`(A_(2))/(A_(1))=(81)/(4)`
When liquid of refractive index `mu` is filled to the right of this lens, the first surface of the lens (radius of curvature `=10cm)` forms the imag at the object only. Considering the refraction at the second surface.
`(mu)/(oo)-(1.5)/(-10)=(mu-1.5)/(10)` (therefore, same area `rArr upsilonrarroo)`
`rArr mu=3`