i. Hydrogen molecule (H2) :

a. Hydrogen atom (Z = 1) has electronic configuration as 1s1.
b. Hydrogen atom contains one electron, hence hydrogen molecule which is diatomic contains two electrons.
c. Linear combination of two 1s atomic orbitals gives rise to two molecular orbitals σ1s and σ*1s.
d. The two electrons from the hydrogen atoms occupy the σ1s molecular orbital and σ*1s remains vacant.
e. Thus, electronic configuration of H2 molecule is σ1s2.
f. Since, no unpaired electron is present in hydrogen molecule, it is diamagnetic.
g. There are no electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital (σ*1s).
h. The bond order of H2 molecule is
Bond order = \(\frac{N_b-N_a}{2}\)
= \(\frac{2-0}{2}\)
= 1
Thus,
A single covalent bond is present between two hydrogen atoms.
[Note : The bond length is 74 pm and the bond dissociation energy is 438 kJ mol-1.]
ii. Lithium molecule (Li2) :
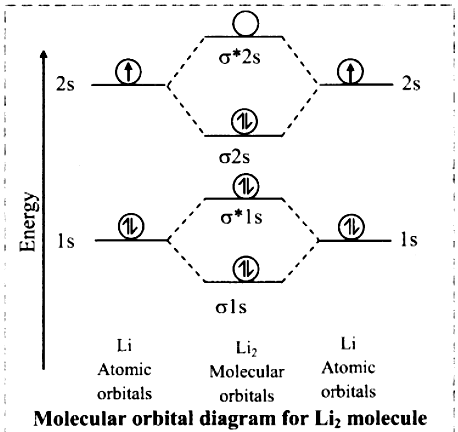
a. Lithium atom (Z = 3) has electronic configuration as 1s2 2s1.
b. Lithium atom has 3 electrons, hence Li2 molecule has 6 electrons.
c. Linear combination of four atomic orbitals gives rise to four molecular orbitals namely σ1s, σ*1s, σ2S and σ*2s.
d. The electronic configuration of Li2 molecule is (σ1s)2 (σ*1s)2 (σ2s)2.
e. Since no unpaired electron is present in lithium molecule, it is diamagnetic.
f. Bond order of Li2 molecule
= \(\frac{N_b-N_a}{2}\)
= \(\frac{4-2}{2}\)
= 1
Thus,
A single covalent bond is present between two Li atoms.
Hence,
Li2 is a stable molecule.