15. Explain what is observed
(i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol.
(ii) An electrolyte, NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol.
(iii) Electric current is passed through a colloidal sol?
Answer:
(i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, then scattering of light is observed. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This scattering of light illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal solution.
(ii) When NaCl is added to ferric oxide sol, it dissociates to give Na+ and Cl- ions. Particles of ferric oxide sol are positively charged. Thus, they get coagulated in the presence of negatively charged Cl- ions.
(iii) The colloidal particles are charged and carry either a positive or negative charge. The dispersion medium carries an equal and opposite charge. This makes the whole system neutral. Under the influence of an electric current, the colloidal particles move towards the oppositely charged electrode. When they come in contact with the electrode, they lose their charge and coagulate.
16. What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give example of each type.
Answer:
The colloidal solution in which both the dispersed phase and dispersion medium are liquids is called an emulsion.
There are two types of emulsions:
(a) Oil in water type:
Here, oil is the dispersed phase while water is the dispersion medium.
For example: milk, vanishing cream, etc.
(b) Water in oil type:
Here, water is the dispersed phase while oil is the dispersion medium.
For example: cold cream, butter, etc.
17. What is demulsification? Name two demulsifiers.
Answer:
The process of decomposition of an emulsion into its constituent liquids is called demulsification.
Examples of demulsifiers are surfactants, ethylene oxide, etc.
18. Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment.
Answer:
The cleansing action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Soaps are basically sodium and potassium salts of long chain fatty acids, R-COO-Na+. The end of the molecule to which the sodium is attached is polar in nature, while the alkyl-end is non-polar. Thus, a soap molecule contains a hydrophilic (polar) and a hydrophobic (nonpolar) part.
When soap is added to water containing dirt, the soap molecules surround the dirt particles in such a manner that their hydrophobic parts get attached to the dirt molecule and the hydrophilic parts point away from the dirt molecule. This is known as micelle formation. Thus, we can say that the polar group dissolves in water while the non-polar group dissolves in the dirt particle. Now, as these micelles are negatively charged, they do not coalesce and a stable emulsion is formed.
19. Give four examples of heterogeneous catalysis.
Answer:
(i) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide to form sulphur trioxide. In this reaction, Pt acts as a catalyst.
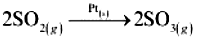
(ii) Formation of ammonia by the combination of dinitrogen and dihydrogen in the presence of finely divided iron.

This process is called the Haber’s process.
(iii) Oswald’s process: Oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide in the presence of platinum.
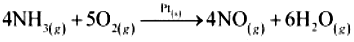
(iv) Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in the presence of Ni.

20. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts?
Answer:
(a) Activity of a catalyst:
The activity of a catalyst is its ability to increase the rate of a particular reaction. Chemisorption is the main factor in deciding the activity of a catalyst. The adsorption of reactants on the catalyst surface should be neither too strong nor too weak. It should just be strong enough to make the catalyst active.
(b) Selectivity of the catalyst:
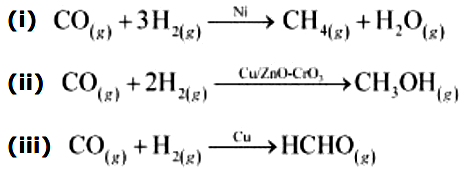
The ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product is referred to as the selectivity of the catalyst. For example, by using different catalysts, we can get different products for the reaction between H2 and CO.
21. Describe some features of catalysis by zeolites.
Answer:
Zeolites are alumino-silicates that are micro-porous in nature. Zeolites have a honeycomblike structure, which makes them shape-selective catalysts. They have an extended 3Dnetwork of silicates in which some silicon atoms are replaced by aluminium atoms, giving them an Al−O−Si framework. The reactions taking place in zeolites are very sensitive to the pores and cavity size of the zeolites. Zeolites are commonly used in the petrochemical industry.
22. What is shape selective catalysis?
Answer:
A catalytic reaction which depends upon the pore structure of the catalyst and on the size of the reactant and the product molecules is called shape-selective catalysis.
For example, catalysis by zeolites is a shape-selective catalysis. The pore size present in the zeolites ranges from 260-740 pm. Thus, molecules having a pore size more than this cannot enter the zeolite and undergo the reaction.
23. Explain the following terms:
(i) Electrophoresis
(ii) Coagulation
(iii) Dialysis
(iv) Tyndall effect.
Answer:
(i) Electrophoresis:
The movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an applied electric field is known as electrophoresis. Positively charged particles move to the cathode, while negatively charged particles move towards the anode. As the particles reach oppositely charged electrodes, they become neutral and get coagulated.
(ii) Coagulation:
The process of settling down of colloidal particles i.e., conversion of a colloid into a precipitate is called coagulation.
(iii) Dialysis:
The process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by the means of diffusion through a membrane is known as dialysis. This process is based on the principle that ions and small molecules can pass through animal membranes unlike colloidal particles.
(iv) Tyndall effect:
When a beam of light is allowed to pass through a colloidal solution, it becomes visible like a column of light. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This phenomenon takes place as particles of colloidal dimensions scatter light in all directions.
24. Give four uses of emulsions.
Answer:
Four uses of emulsions:
(i) Cleansing action of soaps is based on the formation of emulsions.
(ii) Digestion of fats in intestines takes place by the process of emulsification.
(iii) Antiseptics and disinfectants when added to water form emulsions.
(iv) The process of emulsification is used to make medicines.