NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as_________ because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b)In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is _________ type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is _________.
(d)Common detritivores in our ecosystem are_________.
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is_________.
Answer:
(a) Plants are called as autotrophs because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b)In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is of inverted type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for productivity is light.
(d)Common detritivores in our ecosystem are earthworms.
(e) A major reservoir of carbon on Earth is oceans.
2. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
Answer:
(a) Producers
Decomposers include micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi. They form the largest population but they are not included in the food chain. So, producers are the largest one in a food chain.
3. The second trophic level in a lake is
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Answer:
(b) Zooplankton
Zooplankton are primary consumers in aquatic food chains that feed upon phytoplankton. Therefore, they are present at the second trophic level in a lake.
4. Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Plants are the only producers. Thus, they are called primary producers. There are no other producers in a food chain.
5. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation.
(a) 100%
(b) 50 %
(c) 1-5%
(d) 2-10%
Answer:
(b) 50%
Out of total incident solar radiation, about fifty percent of it forms photosynthetically active radiation or PAR.
6. Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid
(d) Food chain and Food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Answer:
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain

(b) Production and decomposition

(c) Upright and inverted pyramid

(d) Food chain and Food web

(e) Litter and detritus

(f) Primary and secondary productivity

7. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is defined as an interacting unit that includes both the biological community as well as the non-living components of an area. The living and the non-living components of an ecosystem interact amongst themselves and function as a unit, which gets evident during the processes of nutrient cycling, energy flow, decomposition, and productivity. There are many ecosystems such as ponds, forests, grasslands, etc. The two components of an ecosystem are:
♦ Biotic component: It is the living component of an ecosystem that includes biotic factors such as producers, consumers, decomposers, etc. Producers include plants and algae. They contain chlorophyll pigment, which helps them carry out the process of photosynthesis in the presence of light. Thus, they are also called converters or transducers. Consumers or heterotrophs are organisms that are directly (primary consumers) or indirectly (secondary and tertiary consumers) dependent on producers for their food. Decomposers include micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi. They form the largest population in a food chain and obtain nutrients by breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals.
♦ Abiotic component: They are the non-living component of an ecosystem such as light, temperature, water, soil, air, inorganic nutrients, etc.
8. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Answer:
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of various ecological parameters such as the number of individuals present at each trophic level, the amount of energy, or the biomass present at each trophic level. Ecological pyramids represent producers at the base, while the apex represents the top level consumers present in the ecosystem. There are three types of pyramids:
- Pyramid of numbers
- Pyramid of energy
- Pyramid of biomass
Pyramid of numbers: It is a graphical representation of the number of individuals present at each trophic level in a food chain of an ecosystem. The pyramid of numbers can be upright or inverted depending on the number of producers. For example, in a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of numbers is upright. In this type of a food chain, the number of producers (plants) is followed by the number of herbivores (mice), which in turn is followed by the number of secondary consumers (snakes) and tertiary carnivores (eagles). Hence, the number of individuals at the producer level will be the maximum, while the number of individuals present at top carnivores will be least.
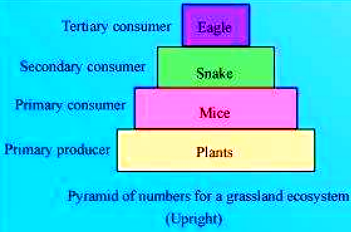
On the other hand, in a parasitic food chain, the pyramid of numbers is inverted. In this type of a food chain, a single tree (producer) provides food to several fruit eating birds, which in turn support several insect species.
Pyramid of biomass: A pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total amount of living matter present at each trophic level of an ecosystem. It can be upright or inverted. It is upright in grasslands and forest ecosystems as the amount of biomass present at the producer level is higher than at the top carnivore level. The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes far exceeds the biomass of zooplankton (upon which they feed).
