Stability of carbanions can be explained by
1. Inductive effect
(a) +I effect

Greater the +I effect, lower is the stability
(b) –I effect

Greater the –I effect, greater is the stability
2. Electronegativity of carbanionic carbon
Stability of carbanion depends on the % S character of carbanionic carbon. Greater the s character, greater is the stability.

3. Delocalisation or Resonance
Allyl and benzyl carbanions are stabilized by delocalisation of negative charge.
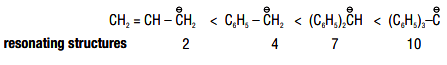
Greater the number of resonating structures, greater is the stability.
Stability of different types of carbanions in decreasing order :
Benzyl carbanion > Allyl carbanion >\(HC\equiv \overset {-}C>H_2C=\overset{-}CH>\) Alkyl carbanion