A dielectric with polar molecules also develops a net dipole moment in an external field, but for a different reason. In the absence of any external field, the different permanent dipoles are oriented randomly due to thermal agitation; so the total dipole moment is zero. When an external field is applied, the individual dipole moments tend to align with the field. When summed over all the molecules, there is then a net dipole moment in the direction of the external field, i.e., the dielectric is polarised. The extent of polarisation depends on the relative strength of two mutually opposite factors: the dipole potential energy in the external field tending to align the dipoles with the field and thermal energy tending to disrupt the alignment. There may be, in addition, the ‘induced dipole moment’ effect as for non-polar molecules, but generally the alignment effect is more important for polar molecules.
Thus in above either case, whether polar or non-polar, a dielectric develops a net dipole moment in the presence of an external field. The dipole moment per unit volume is called polarisation and is denoted by P. For linear isotropic dielectrics,
P = χcE --------- (1)
where χc is a constant characteristic of the dielectric and is known as the electric susceptibility of the dielectric medium. It is possible to relate χc to the molecular properties of the substance,
The polarised dielectric modifies the original external field inside it. To prove this, let us consider a rectangular dielectric slab placed in a uniform external field E0 parallel to two of its faces. The field causes a uniform polarisation P of the dielectric. Thus every volume element Δv of the slab has a dipole moment P Δv in the direction of the field. The volume element Δv is macroscopically small but contains a very large number of molecular dipoles. Anywhere inside the dielectric, the volume element Δv has no net charge (though it has net dipole moment). This is, because, the positive charge of one dipole sits close to the negative charge of the adjacent dipole.
However, at the surfaces of the dielectric normal to the electric field, there is evidently a net charge density. As seen in Fig, the positive ends of the dipoles remain unneutralised at the right surface and the negative ends at the left surface. The unbalanced charges are the induced charges due to the external field.
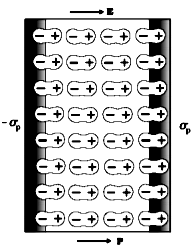
Thus the polarised dielectric is equivalent to two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities, say σp and – σp. Clearly, the field produced by these surface charges opposes the external field. The total field in the dielectric is, thereby, reduced from the case when no dielectric is present. We should note that the surface charge density ± σp arises from bound charges (not free charges) in the dielectric.
If E0 is applied field and EP is the induced field in the dielectric, the net field in the dielectric = EN = E0 - EP.