Equation of the curve is
y = c cos h x/c ......(1)
∴ dy/dx = y1 = sin h x/c .......(2)
and dy1/dx = y2 = (1/c) cos h (x/c) ......(3)
thus p =
 .....(4)
.....(4)
Now portion of the normal intercepted between the curve and the X-axis is
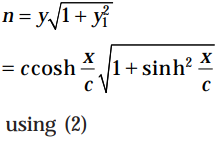
 ......(5)
......(5)
Clearly from eqn (4) and (5) we see that ρ (radius of curvature) = n (length of the normal)
= c cos h2 x/c = y2/c using (1)
∴ ρ varies as square of the ordinate