Consider a sphere of radius
R = (=10cm = 0.1 m) and centre O.
Let the charge on the sphere be ‘q’. Further, let ‘P’ be a point at a distance r = 20cm from the centre of the sphere.
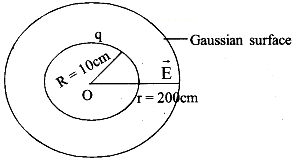
The electric field E( = 1.5 x 103NC-1) is directed radially inward as shown. So as to enclose the charged sphere, draw a sphere (gaussian surface) with the point O as centre and r as the radius. As the electric field is radial, it is normal to the gaussian surface everywhere. Therefore, electric flux through the gaussian surface,
ϕ = -E x area of the gaussian surface
∴ ϕ = -E x 4πr2
= -1.5 x 10-2 x 4π(0.2)2
According to Gauss's theorem,
