(i) Electrophilic substitution reactions of chlorobenzene:
In chlorobenzene, due to -I effect of a chlorine atom, electron density decreases on benzene ring and attack of electrophile occurs slowly. Due to this reason, chlorobenzene is less reactive towards electrophilic substitution reactions in comparison to benzene. Some electrophilic substitution reactions of chlorobenzene are as follows:


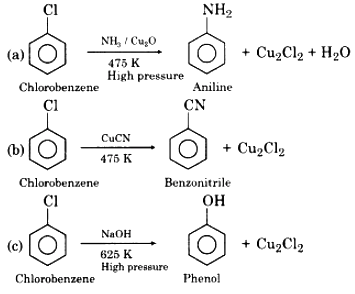
(ii) Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction of Chlorobenzene:
Due to resonance, there is a partial double bond character in the C-X bond of chlorobenzene, as a result, the bond cleavage becomes difficult. Due to this reason, chlorobenzene is less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction than alkyl halides. However, nucleophilic substitution in chlorobenzene occurs under drastic conditions like high-temperature. Some nucleophilic substitution reactions of chlorobenzene are as follows: