Alkanes are chemically inert due to presence of C—H and H—H bond and polar nature. They do not react with acid, base, oxidation, reduction etc. in normal conditions.
General reaction of alkanes :
(i) Combustion : Alkanes burn readily with non-luminous flame in the presence of air or oxygen to form CO2 and water with the evolution of heat.
eg. CH4 + 2O2 ➝ CO2 + 2H2O, ∆H = -ve
(ii) Halogenation: When alkanes react with halogen such chlorine, the replacement of H-atom of alkane by halogen takes place and it forms alkyl halide.
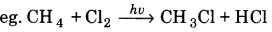
(iii) Isomerization : n-alkanes on heating in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride and HCl gas isomerise to branched chain alkanes.

(iv) Pyrolysis : Higher alkanes on heating to higher temperature decompose into lower alkanes, alkene etc.
