Mitosis: The term Mitosis was proposed by W. Fleming-It is a type of cell division during which a cell divides into two daughter cells. Each containing the similar and same number of chromosomes as present in the parent cell.
Interphase: During this phase doubling of DNA and chromosomes takes place. Interphase is the time between the end of telophase and the beginning of the next phase.
The process of mitosis is studied in two parts:
(1) Karyokinesis
(2) Cytokinesis.
Karyokinesis: Division of the nucleus is called Karyokinesis. During this, many events take place.
Main stages are:
(a) Prophase
(b) Metaphase
(c) Anaphase
(d) Telophase
(a) Prophase: During prophase,
1. Chromosomes become very clear in the form of coiled threads.
2. Chromosomes shorten and become very thick.
3. These chromosomes split up longitudinally into two identical filaments called chromatids. Both the chromatids of a chromosome are attached to a centromere,
4. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus dissolve away,
5. In cells of flowering plants, spindle forms.
(b) Metaphase: All chromosomes arrange themselves on the equatorial plate.
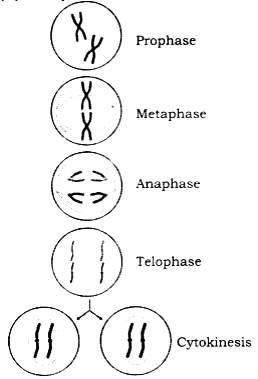
(c) Anaphase: It is the third stage of nucleus division.
1. The centromeres duplicate and split. One centromere is attached to each chromatid. Separated chromatids are now called daughter chromosomes.
2. Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles, by the contraction of the spindle fibres.
(d) Telophase:
1. All the daughter chromosomes after reaching the poles uncoil and become invisible,
2. The nuclear membrane is formed around the chromatin material.
3. Astral rays and spindle disintegrate,
4. Nucleus becomes very distinct and is known as the daughter nucleus,
5. Two daughter cells are formed.
(2) Cytokinesis: Division of the cytoplasm is known as Cytokinesis. After karyokinesis, the somatic cells divide by cell plate method. In a plant cell, minute cytoplasmic vesicles filled up with substances such as calcium and magnesium in pectinate, are arranged in a line in the middle of the equatorial plane and divide the cytoplasm into two parts by progressing from middle to periphery. The cell wall is formed, due to a collection of cellulose on both sides of the plate.
A cleavage furrow appears at the equator of the animal cell and deepens progressively, until the daughter cells separate.