Blackman (1905) formulated the principle of limiting factors. It states that when a metabolic process is conditioned as to its rapidity by a number of separate factors, the rate of the process is limited by the pace of the slowest factor.
This principle is also known as Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors.
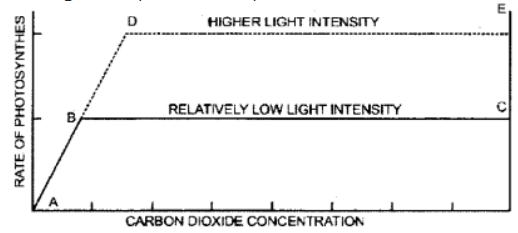
Explanation : A metabolic process is conditioned by a number of factors. The slowest factor or the limiting factor is the one whose increase in magnitude is directly responsible for an increase in the rate of the metabolic process. Let us consider, for example, effect of CO2 and light on the rate of photosynthesis, presuming other factors to be optimum. Suppose a leaf is exposed to a light intensity that allow it (leaf) to reduce 5 mg of carbon (i.e CO2) per hours. If availability of CO2 in the environment is less than the required magnitude, photosynthesis will proceed at a slow rate. Here CO2 becomes the limiting factor in the process of photosynthesis.
If the availability of CO2 is increased there will be corresponding increase in the rate of photosynthesis till the availability of CO2 reaches 5 mg/hr (A- B). Any further increase in CO2 availability will not enhance the rate of photosynthesis because light now becomes a limiting factor (B-C). Thus, while C02 has been limiting the process in reaction, A – B of the graphic curve, light becomes the limiting in the region B-C of the curve. Photosynthetic rate will increase only if there is a corresponding increase in light intensity with the increased concentration of CO2 till CO2 again becomes a limiting factor (A – B, D – E)