(i) 2x – 2y + 3z = 2, x + 2y – z = 3 and 3x – y + 2z = 1
The matrix form of the above equations is

(i.e) AX = B
The augment matrix (A, B) is

The above matrix is in echelon form.
Now writing the equivalent equations

Substituting z = 4 in (2) we get
-6y + 20 = -4
⇒ -6y = -4 – 20 = -24
⇒ y = 4
Substituting z = 4 and y = 4 in (1) we get
x + 8 – 4 = 3
⇒ x + 4 = 3
⇒ x = 3 – 4 = -1
So, x = -1; y = 4; z = 4
(ii) 2x + 4y + 6z = 22 …… (1)
3x + 8y + 5z = 27 ……. (2)
-x + y + 2z = 2 ……. (3)
Divide equation (1) by 2 we get
x + 2y + 3z = 11 ……. (1)
3x + 8y + 5z = 27 …….. (2)
-x + y + 2z = 2 ……. (3)
The matrix form of the above equations is

(i.e) AX = B
The augment matrix (A, B) is
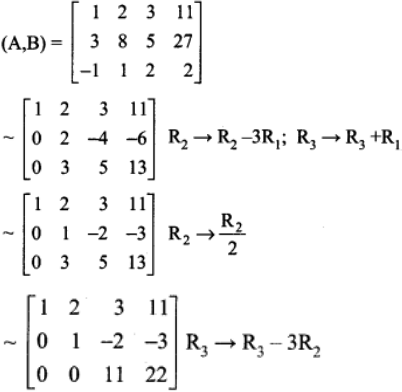
The above matrix is in echelon form.
Now writing the equivalent equations

Substituting z = 2 in (2) we get
y – 4 = -3
⇒ y = -3 + 4 = 1
Substituting z = 2, y = 1 in (1) we get
x + 2(1) + 3(2) = 11
⇒ x + 2 + 6 = 11
⇒ x + 8 = 11
⇒ x = 11 – 8 = 3
x = 3, y = 1, z = 2