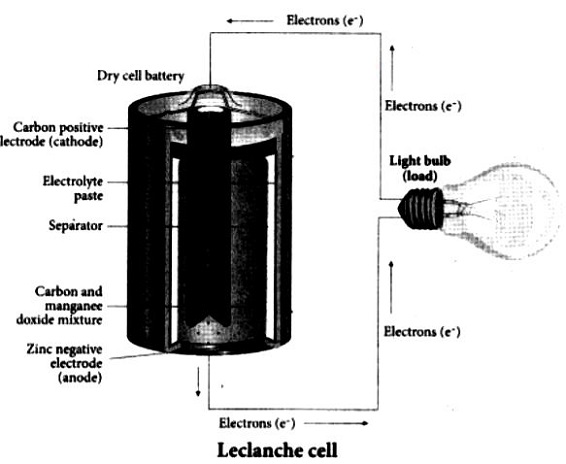
1. Leclanche cell:
Anode: Zinc container Cathode: Graphite rod in contact with MnO2 Electrolyte: Ammonium chloride and Zinc chloride in water.
emf of the cell = 1.5 V
2. Cell reaction:
Oxidation at anode
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e ……(1)
Reduction at cathode
2NH4+(aq) + 2e- → 2NH3(aq) + H2(aq)
3. The hydrogen gas is oxidised to water by
MnO2 H2(g) + 2MnO2(s) → Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l) ……(3)
Adding equations 1,2,3 the overall redox reaction
Zn(s) + 2NH+ + 2MnO2(s) → Zn2+(aq) + Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l) + 2NH3 …………….(4)
4. The ammonia produced at the cathode combines with Zn2+ to form a complex ion [Zn (NH3)4]2+ (aq). As the reaction proceeds, the concentration of NH4+ will decrease and the aqueous NH3 will increase which lead to the decrease in the emf of the cell.