(a) When heated, borax undergoes various transitions. It first loses water molecules and swells. Then, it turns into a transparent liquid, solidifying to form a glass-like material called borax bead.
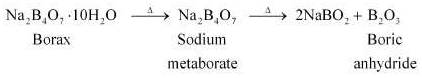
(b) When boric acid is added to water, it accepts electrons from –OH ion. Boric acid is sparingly soluble in cold water however fairly soluble in hot water. boric acid behaves as a weak monobasic acid. It doesn't act as a proton-donor, i.e., protonic acid, however, behaves as a Lewis-acid, i.e., it accepts a pair of electrons.
![B(OH)3+2HOH->[B(OH)4]- + H3O+](https://www.sarthaks.com/?qa=blob&qa_blobid=14552459338046794212)
(c) Al reacts with dilute NaOH to form sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate(III). Hydrogen gas is liberated in the process.

(d) BF3 (a Lewis acid) reacts with NH3 (a Lewis base) to form an adduct. This results in a complete octet around B in BF3.
