Answer :
1. Answer : (a) Etard reaction
Explanation: Thus, oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by the use of chromyl chloride is called Etard's reaction.
2. Answer : (a) nucleophilic addition
Explanation: The reaction of HCN with carbonyl compounds is an example of the nucleophilic addition reaction.
3. Answer : (b) secondary alcohols
Explanation: aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard's reagent to give additional products which on hydrolysis give secondary alcohols.
4. Answer : (c) Benzaldehyde
Explanation: Benzaldehyde will not give aldol condensation due to absence of \(\alpha\)-H atom.
5. Answer : (d) benzaldehyde
Explanation: Benzoyl chloride on reduction with hydrogen in the presence of Pd and `BaSO4 gives acetophenone/ benzaldehyde.
6. Answer : (a) Iodoform test
Explanation: Iodoform test is performed to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one.
7. Answer : (b) 2-Methylpropanal
Explanation: The alpha carbon i.e., the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group is connected to three methyl groups and no hydrogen atom is bonded to it. Thus, the compound has no alpha hydrogen and can undergo a Cannizzaro reaction. Hence, the compound which cannot undergo a Cannizzaro reaction is 2-methylpropanal.
8. Answer : (a) FCH2CHO
Explanation: FCH2CHO is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition since presence of most electrophilic addition since presence of most electronegative F withdraws electrons from carbon of carbonyl group making it more polar.
9. Answer : (c) Aldol
Explanation: Aldehyde and ketones which have at least one \(\alpha\)-hydrogen atom are known to react with dilute aqueous caustic soda. As a result, they produce \(\alpha\)-hydroxy aldehydes. These compounds are known as aldols and reaction is known as aldol reaction.
10. Answer : (c) Dipole-dipole attraction
Explanation: The boiling point of molecules depends on the intermolecular force of attraction, stronger the force, higher is the boiling point. Boiling points of aldehydes and ketone depend on intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction. This is because of electronegative oxygen attached to the carbon atom.
11. Answer : (b) Nucleophiles only
Explanation: The carbonyl group is highly reactive polar group. It is polarised due to the higher electronegativity of oxygen in comparison to carbon. As a result, the electrons present between carbon and oxygen are more attracted towards oxygen atom. The actual structure may be represented as Consequently, the carbonyl carbon is positively charged while the oxygen is negatively charged. The positively charged carbon is easily attacked by a nucleophilic reagent (Nu-).
12. Answer : (b) methyl alcohol
Explanation: When \(\alpha\)-hydrogen is absent in carbonyl group, those compound gives cannizaro reaction. This reaction show disproportionation. The oxidation product is salt of carboxylic acid and reduced product is alcohol.
HCHO + HCHO → CH3OH + HCOO−K+
13. Answer : (a) acetaldehyde
Explanation: Schiff's reagent is used to detect the presence of aldehydic and ketonic group. It consists of fuchsin dye decolourised by sulphurous acid. Immediate red/pink colour appearance detects the presence of aliphatic aldehyde. Aliphatic ketone and aromatic aldehydes takes time and slowly pink colour blooms.
14. Answer : (a) 2-methyl-3-butanone
Explanation: The IUPAC name of CH3COCH(CH3)2 (c) 3-methyl-2-butanone.
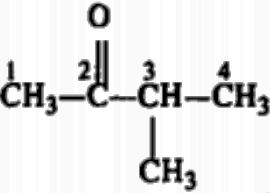
15. Answer: (b) 2-methyl pent-3-one
Explanation: The IUPAC name of ethyl isopropyl ketone is 2-methyl-3-pentanone.
16. Answer: (b) p-p-overlapping
Explanation: π bonds are formed by the sidewise or lateral overlapping of p orbitals. Where, as σ bonds are formed by axial overlapping of molecular orbitals.
17. Answer: (d) Hexanal
Explanation: Hexanal, also called hexanaldehyde or caproaldehyde is an alkyl aldehyde used in the flavor industry to produce fruity flavors. Its scent resembles freshly cut grass, like cis-3-hexenal. It is potentially useful as a natural extract that prevents fruit spoilage.
18. Answer: (a) 2-hydroxy-propane
Explanation: 2-hydroxy propane or secondary alcohol is oxidised into propanone (corresponding because in 2-hydroxy propane, secondary alcoholic group is present and it is oxidised into ketone).
19. Answer: (b) Pd/BaSO4
Explanation: The reaction, a hydrogenolysis, is catalysed by palladium on barium sulfate, which is sometimes called the Rosenmund catalyst. Barium sulfate has a low surface area which reduces the activity of the palladium, preventing over-reduction.
20. Answer: (c) 6 – 8%
Explanation: An aqueous of acetic acid is called vinegar which contains 5-8% acetic acid. Vinegar is a solution of 5-8% acetic acid in water, that's why it is aqueous (containing water) solution of 5%-8% of acetic acid. Other names are Ethanoic acid or Methane carboxylic acid.
21. Answer: (b) NaOH
Explanation: CH3COCH3 + 3I2 + 4NaOH → CHI3 + 3Na + CH3COONa + 3H2O
22. Answer: (c) Cu2O
Explanation: The precipitate formed is red in colour and is only given when Fehling's test is done for aldehyde. Thus, the red precipitate formed when Fehling's solution reacts with aldehyde is Cu2O.
23. Answer: (b) Tollen’s test
Explanation: Tollens' test, also known as silver-mirror test, is a qualitative laboratory test used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone. It exploits the fact that aldehydes are readily oxidized.
24. Answer: (a) Aldehyde
Explanation: Primary alcohols get dehydrogenated with reduced copper at 573K, to give corresponding aldehydes.
25. Answer: (a) NaHSO3
Explanation:

Click here to practice MCQ Question for Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12