The angle bisector of `angleB` meets the opposite side in D.
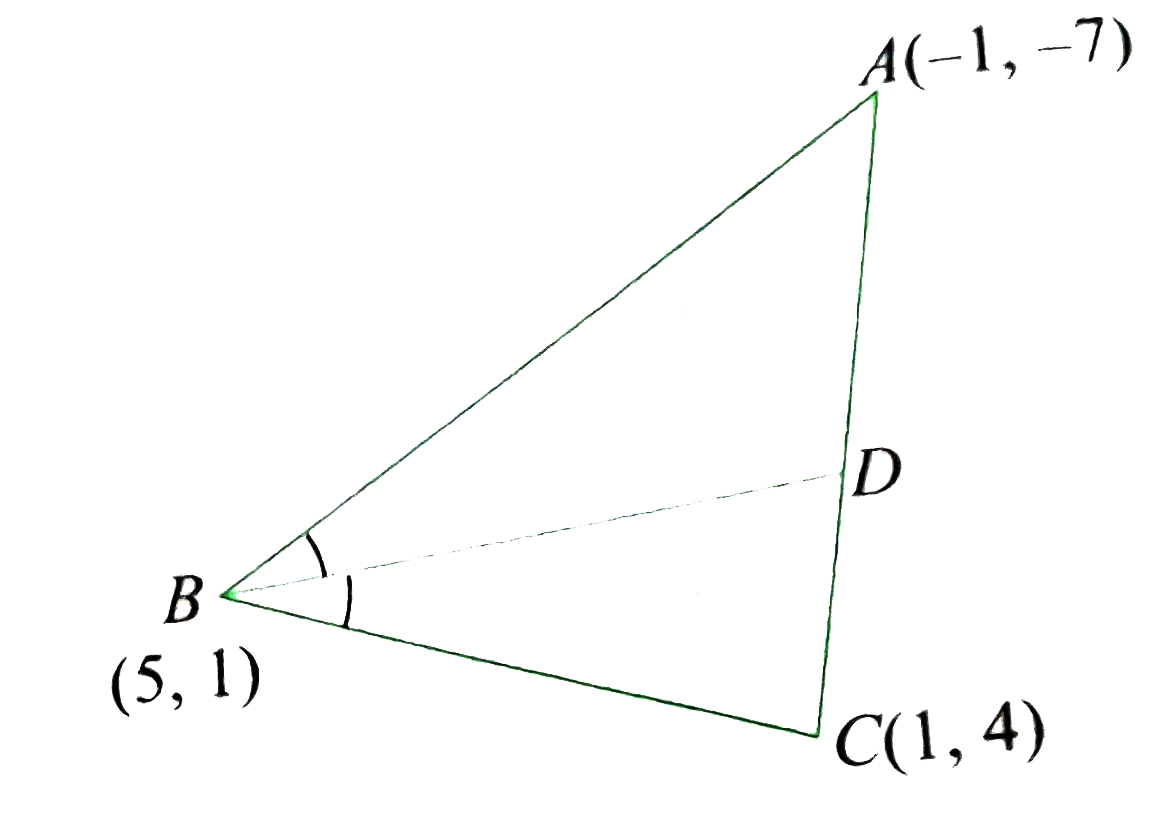
Using angle bisector theorem , we have
`AD:DC=AB:BC`
Now, `AB=sqrt((5+1)^2+(1+7)^2)=10`
and `BC =sqrt((5-1)^2+(1-4)^2)=5`
`therefore D=((2(1)+1(-1))/(2+1),(2(4)+1(-7))/(2+1))=((1)/(3),(1)/(3))`
`therefore BD=sqrt((5-(1)/(3))^2+(1-(1)/(3))^2)=(10sqrt2)/(3)`